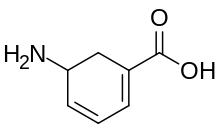
Gabaculine
Each of these studies concluded that gabaculine has a great potential to increase the GABA levels in the brain of these mice in a time dependent manner.
[7] Along with determining the effect of GABA levels, in vivo studies were conducted to investigate the ability of gabaculine to inhibit convulsions in mice.
Results indicated that gabaculine provided a clear anticonvulsant effect against seizures induced by high doses of chemoconvulsants or electroshock.
This study showed that at anticonvulsant doses, gabaculine is extremely potent and toxic when compared to other GABA transaminase inhibitors, with an ED50 of 35 mg/kg and LD50 of 86 mg/kg.
[10] Because of this potential lethal effect, gabaculine was proved to be too toxic for use as a drug however,[8] it can still be used as a compound to alter GABA levels in studies of experimental epilepsy.