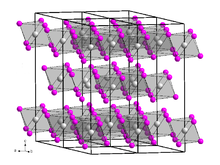
Gadolinium(III) iodide
It is a yellow, highly hygroscopic solid with a bismuth(III) iodide-type crystal structure.
In air, it quickly absorbs moisture and forms hydrates.
The corresponding oxide iodide is also readily formed at elevated temperature.
[2] Gadolinium(III) iodide can be obtained by reacting gadolinium with iodine:[2] It can also be obtained by reacting gadolinium with mercury(II) iodide in a vacuum at 500 °C:[2] Gadolinium(III) iodide can be obtained by the reaction between gadolinium(III) oxide and hydroiodic acid, crystallizing into the hydrate form.
[2][3] Gadolinium(III) iodide reacts with gadolinium and zinc in an argon atmosphere heated to 850 °C to obtain Gd7I12Zn.