Galactic quadrant
The Sun is used instead of the Galactic Center for practical reasons since all astronomical observations (by humans) to date have been based on Earth or within the Solar System.
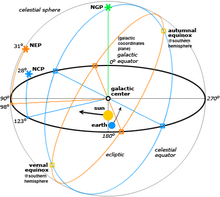
Based on a view from Earth, one may look towards major constellations for a rough sense of where the borders of the quadrants are:[5] (Note: by drawing a line through the following, one can also approximate the galactic equator.)
A long tradition of dividing the visible skies into four precedes the modern definitions of four galactic quadrants.
The Canadian Galactic Plane Survey (CGPS) created a radio map of the Galaxy based on Star Trek's quadrants, joking that "the CGPS is primarily concerned with Cardassians, while the SGPS (Southern Galactic Plane Survey) focuses on Romulans".
As the capital planet of the Republic and later the Empire, Coruscant is used as the reference point for galactic astronomy, set at XYZ coordinates 0-0-0.