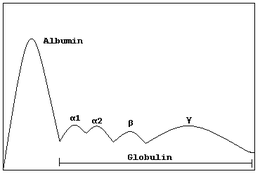
Gamma globulin
Injections are most commonly used on patients having been exposed to hepatitis A or measles, or to make a kidney donor and a recipient compatible regardless of blood type or tissue match.
Overloading the degradation mechanism causes the harmful gamma globulins to have a much shorter half of the life in sera.
[3] Being a product derived from bone marrow and lymph gland cells, gamma globulin injections, along with blood transfusions and intravenous drug use, can pass hepatitis C to their recipients.
However, since hepatitis C is known to have been present since at least the 1940s, a gamma globulin shot received prior to the early 1990s put the recipient at risk of being infected.
Brutton's agammaglobulinemia is an X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections in the early-post natal period attributable to failure of pre-B cells to mature.