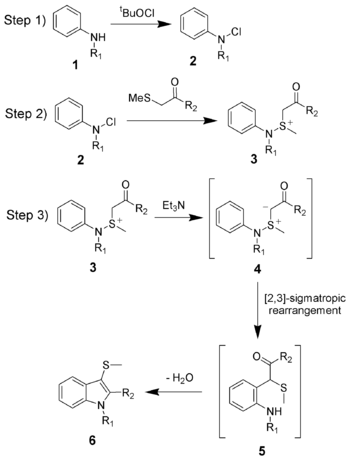
Gassman indole synthesis
The Gassman indole synthesis is a series of chemical reactions used to synthesize substituted indoles by addition of an aniline and a ketone bearing a thioether substituent.
The reaction mechanism of the Gassman indole synthesis is divided among three steps.
The first step is the oxidation of the aniline 1 using tert-butyl hypochlorite (tBuOCl) to give the chloramine 2.
The second step is the addition of the keto-thioether to give the sulfonium ion 3, and is typically done at low temperatures (−78 °C).
Upon warming to room temperature, the base will deprotonate the sulfonium ion creating the sulfonium ylide 4, which quickly undergoes a [2,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give the ketone 5.