Gaussian logarithm
In mathematics, addition and subtraction logarithms or Gaussian logarithms can be utilized to find the logarithms of the sum and difference of a pair of values whose logarithms are known, without knowing the values themselves.
[1] Their mathematical foundations trace back to Zecchini Leonelli[2][3] and Carl Friedrich Gauss[4][1][5] in the early 1800s.
[2][3][4][1][5] The operations of addition and subtraction can be calculated by the formulas where
log
log
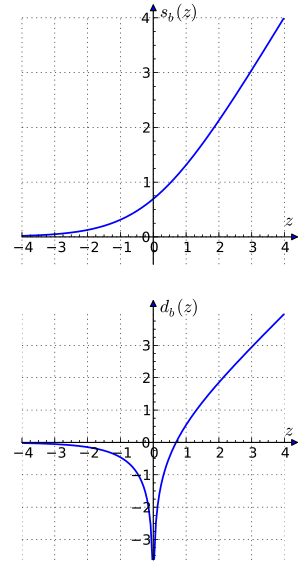
, the "sum" function is defined by
, and the "difference" function by
are also known as Gaussian logarithms.
For natural logarithms with
the following identities with hyperbolic functions exist: This shows that
has a Taylor expansion where all but the first term are rational and all odd terms except the linear term are zero.
The simplification of multiplication, division, roots, and powers is counterbalanced by the cost of evaluating these functions for addition and subtraction.