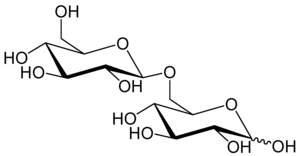
Gentiobiose
Gentiobiose is a disaccharide composed of two units of D-glucose joined with a β(1→6) linkage.
It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water or hot methanol.
[2] During a starch hydrolysis process for glucose syrup, gentiobiose, which has bitterness, is formed as an undesirable product through the acid-catalyzed condensation reaction of two D-glucose molecules.
[3] A further elongation of the unit elongation of the bitter disaccharide by a third β-D-glucose to give the trimer gentiotriose reduces its bitterness by a fifth.
[4] Gentiobiose is also produced via enzymatic hydrolysis of glucans, including pustulan[5] and β-1,3-1,6-glucan.