Gila National Forest
Established in 1905, it now covers approximately 2,710,659 acres (10,969.65 km2), making it the sixth largest national forest in the continental United States.
The Blue Range Primitive Area lies within Arizona in the neighboring Apache National Forest.
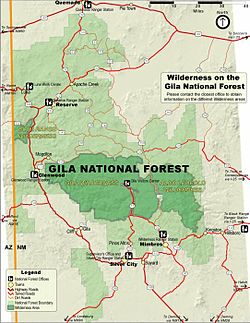
The forest lies in southern Catron, northern Grant, western Sierra, and extreme northeastern Hidalgo counties in southwestern New Mexico.
There are local ranger district offices in Glenwood, Mimbres, Quemado, Reserve, Silver City, and Truth or Consequences.
[3] The Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument is located with the Catron County section of the forest.
The forest's terrain ranges from rugged mountains and deep canyons to mesas and semi-desert.
[4][5] Other notable species include black bear, bald eagle, cougar, Coyote, spotted owl, elk, white-tailed deer, osprey, peregrine falcon, bobcat, collared peccary, Gray fox, white-nosed coati, racoon, mule deer, wild turkey, beaver, desert bighorn sheep, and the endangered Sonoran Pronghorn and Mexican gray wolf,[6][4][5] Hundreds of unregulated cattle roam freely in parts of the Gila National Forest, consuming vegetation by rivers and streams and trampling habitats.