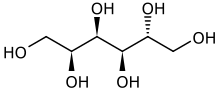
Sorbitol
Sorbitol (/ˈsɔː(r)bɪtɒl/), less commonly known as glucitol (/ˈɡluːsɪtɒl/), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly.
Sorbitol is an isomer of mannitol, another sugar alcohol; the two differ only in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on carbon 2.
The hydrogen atom on NADH is transferred to the electrophilic aldehyde carbon atom; electrons on the aldehyde carbon-oxygen double bond are transferred to the oxygen that abstracts the proton on tyrosine side chain to form the hydroxyl group.
[10] Most bacteria cannot use sorbitol for energy, but it can be slowly fermented in the mouth by Streptococcus mutans, a bacterium that causes tooth decay.
[6] Sorbitol works as a laxative by drawing water into the large intestine, stimulating bowel movements.
[16] A treatment for hyperkalaemia (elevated blood potassium) uses sorbitol and the ion-exchange resin sodium polystyrene sulfonate (tradename Kayexalate).
[18] Sorbitol is also used in the manufacture of softgel capsules to store single doses of liquid medicines.
Sorbitol is used as a cryoprotectant additive (mixed with sucrose and sodium polyphosphates) in the manufacture of surimi, a processed fish paste.
[23] A mixture of sorbitol and potassium nitrate has found some success as an amateur solid rocket fuel.
[24] Sorbitol is identified as a potential key chemical intermediate[25] for production of fuels from biomass resources.
It is also added after electroporation of yeasts in transformation protocols, allowing the cells to recover by raising the osmolarity of the medium.
[6] Common side effects from use as a laxative are stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhea or rectal bleeding.