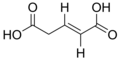
Glutaconic acid
Glutaconate bound to coenzyme A, glutaconyl-CoA, is an intermediate in lysine metabolism.
[1] The geometric isomer, cis-glutaconic acid, has a noticeably lower melting point (130–132 °C).
It can be prepared by bromination of levulinic acid followed by treatment of the dibromoketone with potassium carbonate.
[2] Glutaconic anhydride, which forms by dehydration the diacid, exists mainly as the dicarbonyl tautomer in solution.
In glutaric aciduria type 1, glutaconic acid accumulates, resulting in brain damage.