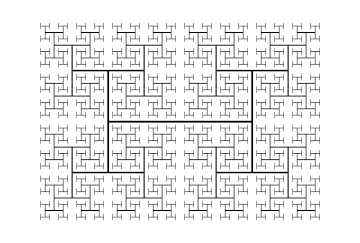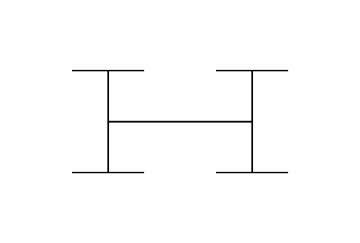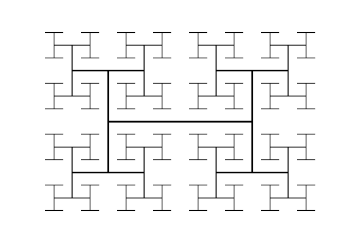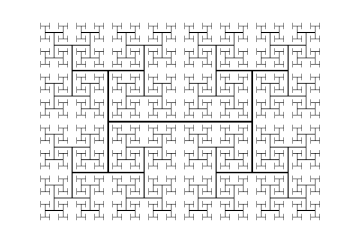
H tree
In fractal geometry, the H tree is a fractal tree structure constructed from perpendicular line segments, each smaller by a factor of the square root of 2 from the next larger adjacent segment.
, but for this variant the resulting shape covers only part of its bounding rectangle, with a fractal boundary.
[2] An alternative process that generates the same fractal set is to begin with a rectangle with sides in the ratio
rectangle leads to the line segment size decreasing uniformly by a
[3] Additionally, the H tree forms a space efficient layout for trees in graph drawing,[4] and as part of a construction of a point set for which the sum of squared edge lengths of the traveling salesman tour is large.
[5] It is commonly used as a clock distribution network for routing timing signals to all parts of a chip with equal propagation delays to each part,[6] and has also been used as an interconnection network for VLSI multiprocessors.
The planar H tree and its three-dimensional version have been found to constitute artificial electromagnetic atoms in photonic crystals and metamaterials and might have potential applications in microwave engineering.
[8] The H tree is an example of a fractal canopy, in which the angle between neighboring line segments is always 180 degrees.
In these variations, to avoid overlaps between the leaves of the tree and their thickened branches, the scale factor by which the size is reduced at each level must be slightly greater than