Hexafluoroethane
The primary aluminium and the semiconductor manufacturing industries are the major emitters of hexafluoroethane using the Hall-Héroult process.
[3] Due to the high energy of C−F bonds, hexafluoroethane is nearly inert and thus acts as an extremely stable greenhouse gas, with an atmospheric lifetime of 10,000 years (other sources: 500 years).
Hexafluoroethane did not exist in significant amounts in the environment prior to industrial-scale manufacturing.
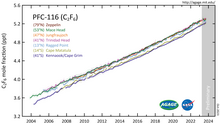
Atmospheric concentration of hexafluoroethane reached 3 pptv at the start of the 21st century.
[5] Its absorption bands in the infrared part of the spectrum cause a radiative forcing of about 0.001 W/m2.