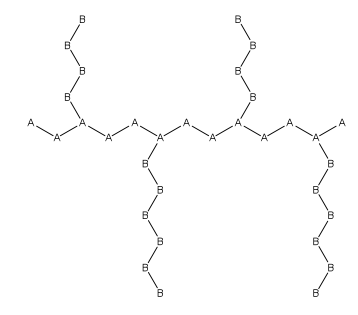
Graft polymer
Graft polymers have been synthesized for many decades and are especially used as impact resistant materials, thermoplastic elastomers, compatibilizers, or emulsifiers for the preparation of stable blends or alloys.
They can be used for materials that are impact resistant, and are often used as thermoplastics elastomers, compatibilizers or emulsifiers for the preparation of stable blends or alloys.
[9] The formation of the graft copolymer originates from the coupling reaction between the functional backbone and the end-groups of the branches that are reactive.
A high yield chemical reaction called atom transfer nitroxide radical coupling chemistry is for the grafting-to method for polymerization.
In the grafting-from method, the macromolecular backbone is chemically modified in order to introduce active sites capable of initiating functionality.
[10] Typically a monomer of a lower molecular weight is copolymerized with free radicals with an acrylate functionalized macromonomer.
The ratio of monomer to macromonomer molar concentrations as well as their copolymerization behavior determines the number of chains that are grafted.
This method allows for branches to be added heterogeneously or homogeneously based on the reactivity ratio of the terminal functional group on the macromolecular to the monomer.
Graft copolymers became widely studied due to their increased number of applications like in drug delivery vehicles, surfactants, water filtration, rheology modifiers, etc.
Some common applications of graft copolymers include: High impact polystyrene (HIPS) was discovered by Charles F. Fryling in 1961.
Its major applications include machined prototypes, low-strength structural components, housings, and covers.