Food chain
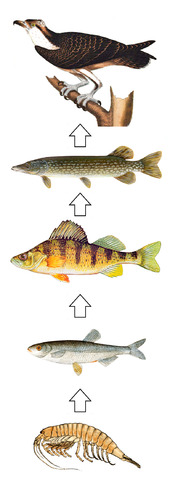
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as earthworms and woodlice), or decomposer (such as fungi or bacteria).
When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction or immense decreases of survival of a species.
[citation needed] Food chain models typically predict that communities are controlled by predators at the top and plants (autotrophs or producers) at the bottom.
Chemosynthetic bacteria and archaea use hydrogen sulfide and methane from hydrothermal vents and cold seeps as an energy source (just as plants use sunlight) to produce carbohydrates; they form the base of the food chain in regions with little to no sunlight.
When any trophic level dies, detritivores and decomposers consume their organic material for energy and expel nutrients into the environment in their waste.
Decomposers and detritivores break down the organic compounds into simple nutrients that are returned to the soil.
Food chains are vital in ecotoxicology studies, which trace the pathways and biomagnification of environmental contaminants.
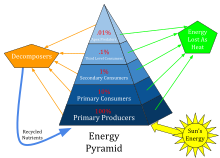
[7] The length of a food chain is a continuous variable providing a measure of the passage of energy and an index of ecological structure that increases through the linkages from the lowest to the highest trophic (feeding) levels.
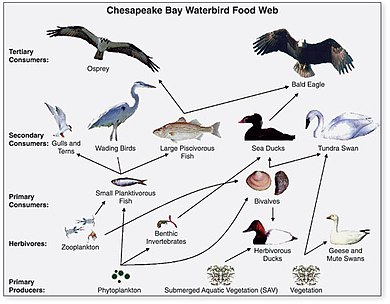
They are simplified abstractions of real food webs, but complex in their dynamics and mathematical implications.
[12] In its simplest form, the length of a chain is the number of links between a trophic consumer and the base of the web.
For example, a food chain might start with a green plant as the producer, which is eaten by a snail, the primary consumer.
[17] Food chain length is important because the amount of energy transferred decreases as trophic level increases; generally only ten percent of the total energy at one trophic level is passed to the next, as the remainder is used in the metabolic process.