Human reproduction
[1] During sexual intercourse, sperm cells are ejaculated into the vagina through the penis, resulting in fertilization of an ovum to form a zygote.
[citation needed] The zygote then undergoes a defined development process that is known as human embryogenesis, and this starts the typical 38-week gestation period[a] for the embryo (and eventually foetus) that is followed by childbirth.
Legal factors also play a vital role in the achievement of human reproduction: a minor under the age of consent cannot give legal consent to sexual intercourse or artificial alternatives to reproduction, the former case of which is liable to have the older party charged with statutory rape, depending on jurisdictions.
[5] The male reproductive system contains two main divisions: the testicles where sperm are produced, and the penis where semen is ejaculated through the urethra.
[6] If the testicles remain too close to the body, it is likely that the increase in temperature will harm the spermatozoa formation, making conception more difficult.
This is why the testes are carried in an external scrotum rather than within the abdomen; they normally remain slightly cooler than body temperature, facilitating sperm production.
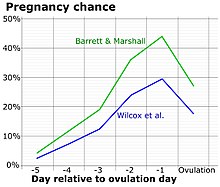
Over a regular interval known as the menstrual cycle, in response to hormonal signals, a process of oogenesis matures one ovum which is released and sent down the fallopian tube.
Oocytes (female germ cells) located in the primordial follicle of the ovary are in a non-growing prophase arrested state, but are able to undergo highly efficient homologous recombinational repair of DNA damages including double-strand breaks.
[8] Human reproduction normally begins with copulation, though it may be achieved through artificial insemination, and is followed by nine months of pregnancy before childbirth.
[18] As an alternative to natural sexual intercourse, there exists artificial insemination, where sperm is introduced into the female reproductive system without the insertion of the penis.
[2] There are also many methods of assisted reproductive technology, such as in vitro fertilization, where one or more egg cells are retrieved from a woman's ovaries and co-incubated with sperm outside the body.
[citation needed] Pregnancy is the period of time during which the fetus develops, dividing via mitosis inside the uterus.
In addition, certain vitamins and other nutrients are required in greater quantities than normal, often creating abnormal eating habits.

1. maturity ; 2. spermatogenesis and oogenesis ; 3. vaginal intercourse with internal fertilization ;
4. zygote ; 5. embryonic development ;
6. childbirth ; 7. adolescence .