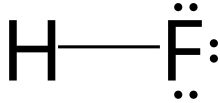Hydrogen fluoride
15 (in DMSO) [2] Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula HF.
It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid.
Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture.
French chemist Edmond Frémy (1814–1894) is credited with discovering hydrogen fluoride (HF) while trying to isolate fluorine.
As a liquid, HF forms relatively strong hydrogen bonds, hence its relatively high boiling point.
However concentrated solutions are strong acids, because bifluoride anions are predominant, instead of ion pairs.
Like water, HF can act as a weak base, reacting with Lewis acids to give superacids.
It is used in the majority of the installed linear alkyl benzene production facilities in the world.
The process involves dehydrogenation of n-paraffins to olefins, and subsequent reaction with benzene using HF as catalyst.
Breathing in hydrogen fluoride at high levels or in combination with skin contact can cause death from an irregular heartbeat or from pulmonary edema (fluid buildup in the lungs).