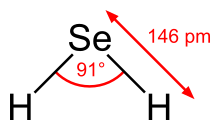
Hydrogen selenide
[8] A number of routes to H2Se have been reported, which are suitable for both large and small scale preparations.
In the laboratory, H2Se is usually prepared by the action of water on Al2Se3, concomitant with formation of hydrated alumina.
[9] H2Se can also be prepared by means of different methods based on the in situ generation in aqueous solution using boron hydride, Marsh test and Devarda's alloy.
Illustrative is the synthesis of selenoureas from cyanamides:[11] H2Se gas is used to dope semiconductors with selenium.
[5] Exposure at high concentrations, even for less than a minute, causes the gas to attack the eyes and mucous membranes; this causes cold-like symptoms for at least a few days afterwards.