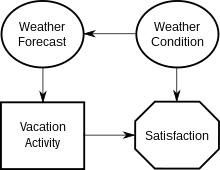
Influence diagram
ID was first developed in the mid-1970s by decision analysts with an intuitive semantic that is easy to understand.
It is now adopted widely and becoming an alternative to the decision tree which typically suffers from exponential growth in number of branches with each variable modeled.
Consider the simple influence diagram representing a situation where a decision-maker is planning their vacation.
The above example highlights the power of the influence diagram in representing an extremely important concept in decision analysis known as the value of information.
The applicability of this simple ID and the value of information concept is tremendous, especially in medical decision making when most decisions have to be made with imperfect information about their patients, diseases, etc.
An ID that is consistently defined at all levels—structure, function, and number—is a well-defined mathematical representation and is referred to as a well-formed influence diagram (WFID).
WFIDs can be evaluated using reversal and removal operations to yield answers to a large class of probabilistic, inferential, and decision questions.
More recent techniques have been developed by artificial intelligence researchers concerning Bayesian network inference (belief propagation).