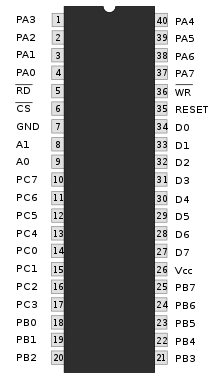
Intel 8255
The 8255 provides 24 parallel input/output lines with a variety of programmable operating modes.
The 8255 is a member of the MCS-85 family of chips, designed by Intel for use with their 8085 and 8086 microprocessors and their descendants.
[2] It found wide applicability in digital processing systems and was later cloned by other manufacturers.
The 82C55 is a CMOS version for higher speed and lower current consumption.
The functionality of the 8255 is now mostly embedded in larger VLSI processing chips as a sub-function.
Other comparable microprocessor I/O chips are the 2655 Programmable Peripheral Interface from the Signetics 2650 family, the Z80 PIO, the Western Design Center WDC 65C21 (equivalent to the Motorola 6820/6821), and the MOS Technology 6522 VIA and 6526 CIA which had considerable additional functionality such as timers and shift registers.
[5] The available 82C55A CMOS version was outsourced to Oki Electronic Industry Co., Ltd.[6] The available package from Intel branded 82C55 in 44-pin PLCC of sampling at fourth quarter of 1985.
[7] In Eastern Europe, equivalent circuits were manufactured as the KR580VV55A in the Soviet Union and as the MHB8255A by Tesla in Czechoslovakia.
WR (pin 36), which are active-low signals for read and write operations respectively.
This is done to prevent 8255 and/or any peripheral connected to it from being destroyed due to mismatch of port direction settings.
If from the previous operation, port A is initialized as an output port and if 8255 is not reset before using the current configuration, then there is a possibility of damage of either the input device connected or 8255 or both, since both 8255 and the device connected will be sending out data.
Each line of port C (PC7 - PC0) can be set or reset by writing a suitable value to the control word register.
The input/output features in mode 0 are as follows: 'Latched' means the bits are put into a storage register (array of flip-flops) which holds its output constant even if the inputs change after being latched.
In this mode, the 8255 may be used to extend the system bus to a slave microprocessor or to transfer data bytes to and from a floppy disk controller.