Intragovernmental holdings
These agencies may receive or spend money unevenly throughout the year, or receive it for payout at a future date, as in the case of a pension fund.
Lending the excess funds to the government, typically on the accounts of its treasury, enables the government to calculate its net cash requirements over time.
In the United States, intragovernmental holdings are primarily composed of the Medicare trust funds, the Social Security Trust Fund, and Federal Financing Bank securities.
A small amount of marketable securities are held by government accounts.
[1][2] US specific: https:/.ticdata.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/tic/Document/slt_table5.txt This finance-related article is a stub.
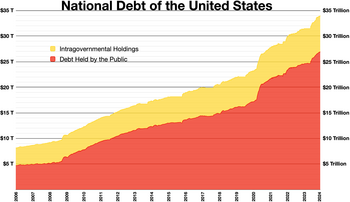
National debt of the United States
Intragovernmental holdings
Debt held by the
public
