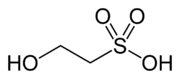
Isethionic acid
Its discovery is generally attributed to Heinrich Gustav Magnus, who prepared it by the action of solid sulfur trioxide on ethanol in 1833.
The original synthesis of the compound, involving the reaction of sulfur trioxide with ethanol, has largely been replaced by more advanced methods.
An alternative production method involves the hydrolysis of carbyl sulfate, which is derived from the sulfonation of ethylene.
Isethionic acid is also used as a counter ion in certain pharmaceutical formulations, including the antimicrobials hexamidine and pentamidine.
[5] Studies made on dog heart slices suggested that heart tissue may be capable of converting taurine to isethionic acid, further experiments demonstrated that this tissue may synthesize taurine from cystine.