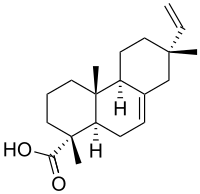
Isopimaric acid
IPA originates from many sorts of trees, especially conifers.
[1] IPA is one of the members of the resin acid group and it is a tricyclic diterpene.
In this state BK channels can still be inhibited by one of their inhibitors, like charybdotoxin (CTX).
[2][3] Opening of the BK channel leads to an increased K+-efflux which hyperpolarizes the resting membrane potential, reducing the excitability of the cell in which the BK-channel is expressed.
Studies on rainbow trout hepatocytes have shown that IPA increases intracellular calcium release, leading to a disturbance in the calcium homeostasis.