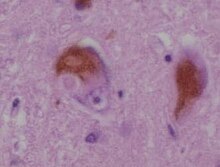
Lewy body
A classical Lewy body is an eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion consisting of a dense core surrounded by a halo of 10 nm wide radiating fibrils, the primary structural component of which is alpha-synuclein (α-synuclein).
While similar in many other respects, cortical Lewy bodies are only faintly eosinophilic, do not have a surrounding halo, and do not show a radial filamentous substructure.
[5] Konstantin Nikolaevich Trétiakoff found them in 1919 in the substantia nigra of PD brains, called them corps de Lewy and is credited with the eponym.
[6] Eliasz Engelhardt, who is in the neurology department at Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, argued in 2017 that Lafora should be credited with the eponym, because he named them six years before Trétiakoff.
[16] Aggregation is believed to occur when there is a high amount of misfolded proteins in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, which are then brought to a resulting aggresome so they can be organized into one place.
Despite their differences, there is evidence that a particular protein family, called 14-3-3, plays a role in the formation of both cortical and classical Lewy bodies.
[17][better source needed] This makes it an important protein family in regards to Lewy body-associated diseases, and there are at least 7 forms of it that have been clearly identified in mammals.