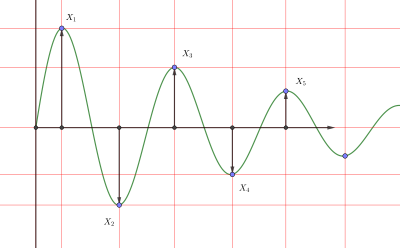
Logarithmic decrement
, is used to find the damping ratio of an underdamped system in the time domain.
The method of logarithmic decrement becomes less and less precise as the damping ratio increases past about 0.5; it does not apply at all for a damping ratio greater than 1.0 because the system is overdamped.
The logarithmic decrement is defined as the natural log of the ratio of the amplitudes of any two successive peaks: where x(t) is the overshoot (amplitude - final value) at time t and x(t + nT) is the overshoot of the peak n periods away, where n is any integer number of successive, positive peaks.
The damping ratio is then found from the logarithmic decrement by: Thus logarithmic decrement also permits evaluation of the Q factor of the system: The damping ratio can then be used to find the natural frequency ωn of vibration of the system from the damped natural frequency ωd: where T, the period of the waveform, is the time between two successive amplitude peaks of the underdamped system.
The method of fractional overshoot can be useful for damping ratios between about 0.5 and 0.8.