Longest common substring
In computer science, a longest common substring of two or more strings is a longest string that is a substring of all of them.
Applications include data deduplication and plagiarism detection.
The picture shows two strings where the problem has multiple solutions.
Although the substring occurrences always overlap, it is impossible to obtain a longer common substring by "uniting" them.
The strings "ABABC", "BABCA" and "ABCBA" have only one longest common substring, viz.
Other common substrings are "A", "AB", "B", "BA", "BC" and "C".
, find a longest string which is substring of both
A generalization is the k-common substring problem.
, a longest string which occurs as substring of at least
One can find the lengths and starting positions of the longest common substrings of
time with the help of a generalized suffix tree.
A faster algorithm can be achieved in the word RAM model of computation if the size
[1] Solving the problem by dynamic programming costs
The solutions to the generalized problem take
time with dynamic programming and take
time with a generalized suffix tree.
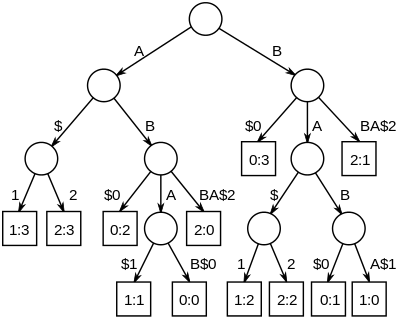
The longest common substrings of a set of strings can be found by building a generalized suffix tree for the strings, and then finding the deepest internal nodes which have leaf nodes from all the strings in the subtree below it.
The figure on the right is the suffix tree for the strings "ABAB", "BABA" and "ABBA", padded with unique string terminators, to become "ABAB$0", "BABA$1" and "ABBA$2".
The nodes representing "A", "B", "AB" and "BA" all have descendant leaves from all of the strings, numbered 0, 1 and 2.
Building the suffix tree takes
time (if the size of the alphabet is constant).
If the tree is traversed from the bottom up with a bit vector telling which strings are seen below each node, the k-common substring problem can be solved in
If the suffix tree is prepared for constant time lowest common ancestor retrieval, it can be solved in
[2] The following pseudocode finds the set of longest common substrings between two strings with dynamic programming: This algorithm runs in
The array L stores the length of the longest common suffix of the prefixes S[1..i] and T[1..j] which end at position i and j, respectively.
The variable z is used to hold the length of the longest common substring found so far.
The set ret can be saved efficiently by just storing the index i, which is the last character of the longest common substring (of size z) instead of S[(i-z+1)..i].
The following tricks can be used to reduce the memory usage of an implementation: