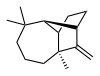
Longifolene
It is an oily liquid hydrocarbon found primarily in the high-boiling fraction of certain pine resins.
The enantiomer commonly found in pines and other higher plants exhibits a positive optical rotation of +42.73°.
The other enantiomer (optical rotation −42.73°) is found in small amounts in certain fungi and liverworts.
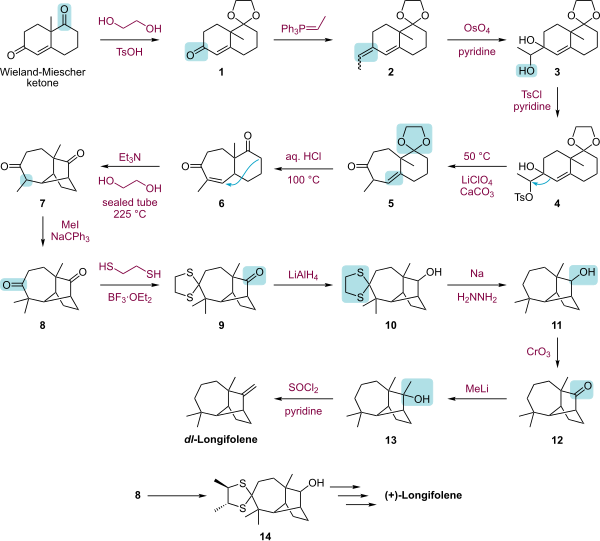
The laboratory characterization and synthesis of longifolene has long attracted attention.
[4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11] It reacts with borane to give the derivative dilongifolylborane, which is a chiral hydroborating agent.