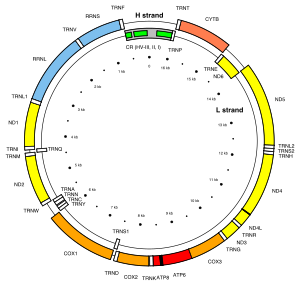
MT-ND4
[6] Variations in the MT-ND4 gene are associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD), Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) and cystic fibrosis.
MT-ND4 is a subunit of the respiratory chain Complex I that is believed to belong to the minimal assembly of core proteins required to catalyze NADH dehydrogenation and electron transfer to ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10).
[14] Initially, NADH binds to Complex I and transfers two electrons to the isoalloxazine ring of the flavin mononucleotide (FMN) prosthetic arm to form FMNH2.
This provides a simple diagnostic test by which to identify LHON, a maternally inherited disease that results in optic nerve degeneration and cardiac dysrythmia.
[9] Amino acid changes in MT-ND4, MT-ND5 and MT-ATP8 resulting from mutations at the 11994, 8502 and 13,231 bp of mtDNA are significantly correlated in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) patients with hippocampal sclerosis.