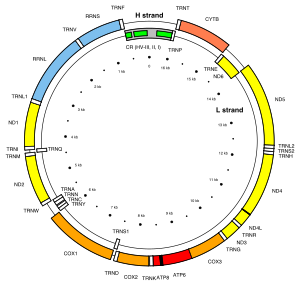
MT-ND4L
[5] The ND4L protein is a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), which is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain.
The MT-ND4L product is a subunit of the respiratory chain Complex I that is believed to belong to the minimal assembly of core proteins required to catalyze NADH dehydrogenation and electron transfer to ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10).
[12] Initially, NADH binds to Complex I and transfers two electrons to the isoalloxazine ring of the flavin mononucleotide (FMN) prosthetic arm to form FMNH2.
[6] Mitochondrial dysfunction resulting from variants of MT-ND4L, MT-ND1 and MT-ND2 have been linked to BMI in adults and implicated in metabolic disorders including obesity, diabetes and hypertension.
This mutation results in the replacement of the amino acid valine with alanine at position 65 of the protein ND4L, disrupting function of Complex I in the electron transport chain.