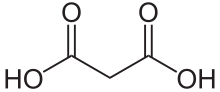
Malonic acid
[7] This led to priority dispute with Hans Hübner and Maxwell Simpson who had independently published preliminary results on related reactions.
[7] The structure has been determined by X-ray crystallography[8] and extensive property data including for condensed phase thermochemistry are available from the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
It can also be a component in alkyd resins, which are used in a number of coatings applications for protecting against damage caused by UV light, oxidation, and corrosion.
[20] The global coatings market for automobiles was estimated to be $18.59 billion in 2014 with projected combined annual growth rate of 5.1% through 2022.
In 2004, annual global production of malonic acid and related diesters was over 20,000 metric tons.
In 2004, malonic acid was listed by the US Department of Energy as one of the top 30 chemicals to be produced from biomass.
[27] Eastman Kodak company and others use malonic acid and derivatives as a surgical adhesive.
[30][31] Additionally, the coenzyme A derivative of malonate, malonyl-CoA, is an important precursor in cytosolic fatty acid biosynthesis along with acetyl CoA.
Malonic acid is the classic example of a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (complex II), in the respiratory electron transport chain.
[32] It binds to the active site of the enzyme without reacting, competing with the usual substrate succinate but lacking the −CH2CH2− group required for dehydrogenation.
[33][34] Since malonic acid is a natural component of many foods, it is present in mammals including humans.