Management of Parkinson's disease
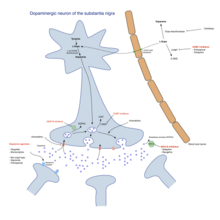
[3] Treatment in the initial state aims to attain an optimal tradeoff between good management of symptoms and side effects resulting from enhancement of dopaminergic function.
[3] A similar drug, entacapone, has not been shown to cause significant alterations of liver function and maintains adequate inhibition of COMT over time.
Levodopa preparations lead in the long term to the development of motor complications characterized by involuntary movements called dyskinesias and fluctuations in the response to medication.
[medical citation needed] In animal models it was shown that the intake of adenosine receptor antagonists together with levodopa can amplify its therapeutic effects.
After an initial "apomorphine challenge" in hospital to test its effectiveness and brief patient and primary caregiver (often a spouse or partner), the latter of whom takes over maintenance of the pump.
[medical citation needed] Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (selegiline and rasagiline) increase the level of dopamine in the basal ganglia by blocking its metabolization.
[18] Parkinson UK found: Muscles and nerves that control the digestive process may be affected by PD, so it is common to experience constipation and gastroparesis (food remaining in the stomach for a longer period of time than normal).
[20] Therefore, when levodopa is introduced, excessive proteins are discouraged, while in advanced stages, additional intake of low-protein products such as bread or pasta is recommended for similar reasons.
[21] Studies in the past few decades have led to great improvements in surgical techniques, and surgery is again being used in people with advanced PD for whom drug therapy is no longer sufficient.
The IPG, which is battery-powered and encased in titanium, is traditionally implanted under the collarbone, and is connected by the subcutaneous extension to the lead, which extends from outside the skull under the scalp down into the brain to the target of stimulation.
The indirect method uses computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ventriculography to locate the anterior and posterior commissures and then employs predetermined coordinates and distances from the intercommissural line to define the target area.
[23] Electrophysial functional mapping, a tool used in both methods to verify the target nuclei, has come under scrutiny due to its associated risks of hemorrhages, dysarthria or tetanic contractions.
Recently, susceptibility-weighted imaging, a type of MRI, has shown incredible power in its ability to distinguish these deep brain nuclei and is being used in DBS to reduce the overuse of EFM.
Exercise interventions have been shown to benefit patients with Parkinson's disease in regards to physical functioning, health-related quality of life, and balance and fall risk.
[25] Occupational therapy (OT) aims to promote health and quality of life by helping people with the disease to participate in as many activities of their daily living as possible.
[33] In terms of improving flexibility and range of motion for patients experiencing rigidity, generalized relaxation techniques such as gentle rocking have been found to decrease excessive muscle tension.
[34] Common changes in gait associated with the disease such as hypokinesia (slowness of movement), shuffling and decreased arm swing are addressed by a variety of strategies to improve functional mobility and safety.
[36] An 8-week resistance training study geared towards the lower legs found that patients with Parkinson's Disease gained abdominal strength, and improved in their stride length, walking velocity and postural angles.
[37] Also, due to the forward flexed posture and respiratory dysfunctions in advanced Parkinson's disease, deep diaphragmatic breathing exercises are beneficial for improving chest wall mobility and vital capacity.
Compared to no intervention, single sessions of WBV have resulted in improved motor ability, as reflected by Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) tremor and rigidity scores.
[45] Treating Parkinson's disease engages a multidisciplinary approach, and includes a psychologist, because motor symptoms can be worsened by psychosocial factors like anxiety, phobia, and panic attacks.
[46] Since it is proven that tremor-dominant and akinetic rigid types of Parkinson's disease have various different visuomotor deficiencies, like problems in visual perception and motor coordination, that can influence their gait training, it is recommended for them to receive neuropsychological assessment before physical therapy.
Previous research studies have utilized body weight support systems during gait training, where individuals are suspended from an overhead harness with straps around the pelvic girdle as they walk on a treadmill.
One solution proposed to reduce social and economic barriers to access to remote care is to establish satellite teleneurology clinics in underserved regions.
[74] Such research directions include the search of new animal models of the disease, and the potential usefulness of gene therapy, stem cells transplants, and neuroprotective agents.
[75] The tragedy of a group of drug addicts in California in the early 1980s who consumed a contaminated and illicitly produced batch of the synthetic opiate MPPP brought to light MPTP as a cause of parkinsonian symptoms.
[80] The study showed the first success of randomised, double-blind gene therapy trial for a neurodegenerative disease and justified the continued development of AAV2-GAD for treatment of PD.
This protection can occur before any symptoms manifest based on genetic risk, and also during early- or late-stage PD when other treatments have ceased their impact due to the progression of the disease.
[75] Agents currently under investigation include antiapoptotics (omigapil, CEP-1347), antiglutamatergics, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (selegiline, rasagiline), promitochondrials (coenzyme Q10, creatine), calcium channel blockers (isradipine) and growth factors (GDNF).
In response to potentially toxic amphetamine metabolites caused by selegiline, another promising treatment is in MAO B propargyl amine inhibitor rasagiline (N-propargyl-1-R-aminoindan, Azilect((R))).