Materials Adherence Experiment
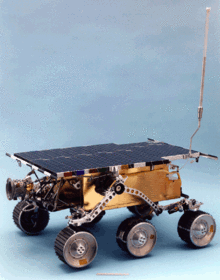
[1] This was a joint experiment between NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology[2] that consisted of a small module mounted to Pathfinder's rover Sojourner that examined the effects of Martian surface dust on solar cells.
[3] In addition to blocking sunlight from reaching Mars's surface, dust particles gradually settle out of the air and onto objects.
As the mission progressed, atmospheric dust would settle on the glass cover plate, blocking increasingly more sunlight from striking the solar cell, causing it to produce less power.
[3] The rotating actuator used to move the glass cover plate away from the solar cell marked the first use of a multi-cycle shape memory alloy in a space application.
[3] Due to the high level of UV radiation on the surface of Mars, it was important that the glass that covered the solar cell would not darken.