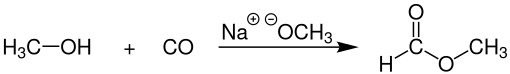Methyl formate
The simplest example of a carboxylate ester, it is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension.
[4] In the laboratory, methyl formate can be produced by the condensation reaction of methanol and formic acid, as follows: Industrial methyl formate, however, is usually produced by the combination of methanol and carbon monoxide (carbonylation) in the presence of a strong base, such as sodium methoxide:[4] This process, practiced commercially by BASF among other companies gives 96% selectivity toward methyl formate.
The catalyst for this process is sensitive to water, which can be present in the carbon monoxide feedstock, which is commonly derived from synthesis gas.
[5] Methyl formate is used primarily to manufacture formamide, dimethylformamide, and formic acid.
[citation needed] A historical use of methyl formate, which sometimes brings it attention, was in refrigeration.