Mitotic inhibitor
Microtubules are created during normal cell functions by assembling (polymerizing) tubulin components, and are disassembled when they are no longer needed.
[2][3] Tubulin binding molecules have generated significant interest after the introduction of the taxanes into clinical oncology and the general use of the vinca alkaloids.
Examples of mitotic inhibitors frequently used in the treatment of cancer include paclitaxel, docetaxel, vinblastine, vincristine, and vinorelbine.
[4] They play a critical role in cell division by their involvement in the movement and attachment of chromosomes during various stages of mitosis.
The tubulin hetero-dimers arrange themselves in a head to tail manner with the α-subunit of one dimer coming in contact with the β-subunit of the other.
About 12–13 protofilaments arrange themselves in parallel to form a C-shaped protein sheet, which then curls around to give a pipe-like structure called the microtubule.
A microtubule exists in a continuous dynamic state of growing and shortening by reversible association and dissociation of α/β-tubulin heterodimers at both the ends.
This dynamic behavior and resulting control over the length of the microtubule is vital to the proper functioning of the mitotic spindle in mitosis i.e., cell division.
The other class of inhibitors operate by inhibiting the depolymerization of polymerized tubulin and increases the microtubule polymer mass in the cells.
This complex brings about a conformational change which blocks the tubulin dimers from further addition and thereby prevents the growth of the microtubule.
As the T-C complex slows down the addition of new dimers, the microtubule disassembles due to structural imbalance or instability during the metaphase of mitosis.
[13] The Vinca alkaloids bind to the β-subunit of tubulin dimers at a distinct region called the Vinca-binding domain.
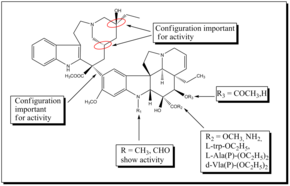
The stability of the tropone ring and the position of the methoxy and carbonyl group are crucial for the binding ability of the compound.
[13] Paclitaxel has achieved great success as an anti-cancer drug, yet there has been continuous effort to improve its efficacy and develop analogues which are more active and have greater bioavailability and specificity.
Most of the SAR studies involve the vindoline portion of bis-indole alkaloids because modification at C-16 and C-17 offers good opportunities for developing new analogues.
Similarly replacement of the acetyl group at C-16 with L-trp-OC2H5, d-Ala(P)-(OC2H5)2, L-Ala(P)-(OC2H5)2 and I-Vla(P)-(OC2H5)2 gave rise to new analogues having anti- tubulin activity.
Also it was found that the vindoline's indole methyl group is a useful position to functionalize potentially and develop new, potent vinblastine derivatives.
Tubulin binding molecules differ from the other anticancer drugs in their mode of action because they target the mitotic spindle and not the DNA.
b) Vinca alkaloids binding site,[19] includes vinblastine, vincristine, vinorelbine, vinflunine, dolastatins, halichondrins, hemiasterlins, cryptophysin 52, etc.
Dissolution of microtubules subsequently was shown to be responsible for the effect of colchicine on the mitotic spindle and cellular proliferation.
It inhibits the assembly of fungal microtubules Limitations in anticancer therapy occur mainly due to two reasons; because of the patient's organism, or because of the specific genetic alterations in the tumor cells.
From the patient, therapy is limited by poor absorption of a drug which can lead to low concentration of the active agent in the blood and small amount delivery to the tumor.
Low serum level of a drug can be also caused by rapid metabolism and excretion associated with affinity to intestinal or/and liver cytochrome P450.
This protein is a product of multidrug resistance gene MDR1 and a member of family of ATP-dependent transporters (ATP-binding cassette).
The next step is hydrolysis of ATP, which leads to a change in the shape of P-gp and opens a channel through which the drug is pumped out of the cell.
It was discovered that another transporter MRP1 also work as the efflux pump, but in this case substrates are negatively charged natural compounds or drugs modified by glutathione, conjugation, glycosylation, sulfation and glucuronylation.
In addition tumor cells express other kinds of proteins and change microtubule dynamic to counteract effect of anticancer drugs.
They were isolated from extracts leaves of the Catharanthus roseus (Vinca rosea) plant at the University of Western Ontario in 1958.
[5] First drug belong to the taxanes and paclitaxel, discovered in extracts from the bark of the yew tree, Taxus brevifolia, in 1967 by Monroe Wall and Mansukh Wani but, its tubulin inhibition activity was not known until 1979.
Yews trees are poor source of active agents that limited the development of taxanes for over 20 years until discover the way of synthesis.