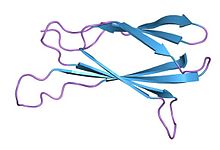
Monobody
Monobodies are synthetic binding proteins constructed using a fibronectin type III domain (FN3) as a molecular scaffold.
Specifically, this class of binding proteins are built upon a diversified library of the 10th FN3 domain of human fibronectin.
An example is pegdinetanib (Angiocept), an antagonist of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), which has entered Phase II clinical trials investigating the treatment of glioblastoma in October 2007.
They are based on the structure of human fibronectin, more specifically on its tenth extracellular type III domain.
Monobodies with high affinity and specificity for different target molecules can be generated from combinatorial libraries in which portions of the FN3 scaffold are diversified.