Monoclonal antibody
[3] In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages.
It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to almost any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it.
Ehrlich and Élie Metchnikoff received the 1908 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for providing the theoretical basis for immunology.
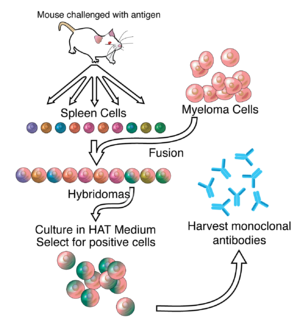
By the 1970s, lymphocytes producing a single antibody were known, in the form of multiple myeloma – a cancer affecting B-cells.
By the 1990s research was making progress in using monoclonal antibodies therapeutically, and in 2018, James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery of cancer therapy by inhibition of negative immune regulation, using monoclonal antibodies that prevent inhibitory linkages.
He is a true translational investigator, since he used these monoclonal antibodies to classify human B-cell leukemia and lymphomas as well as to create therapeutic agents for patients.
This is possible because myeloma cells have lost the ability to synthesize hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT), an enzyme necessary for the salvage synthesis of nucleic acids.
Cell culture sample contaminants consist primarily of media components such as growth factors, hormones and transferrins.
Depending on the complexity of the media required in cell culture and thus the contaminants, one or the other method (in vivo or in vitro) may be preferable.
In addition, the concentration of product in the sample may not be sufficient, especially in cases where the desired antibody is produced by a low-secreting cell line.
Since we are dealing with proteins, properties such as charge and affinity are not consistent and vary with pH as molecules are protonated and deprotonated, while size stays relatively constant.
In addition to possibly affecting the product, low pH can cause protein A/G itself to leak off the column and appear in the eluted sample.
Gentle elution buffer systems that employ high salt concentrations are available to avoid exposing sensitive antibodies to low pH.
To achieve maximum purity in a single step, affinity purification can be performed, using the antigen to provide specificity for the antibody.
If the antigen is a peptide, it is commonly synthesized with a terminal cysteine, which allows selective attachment to a carrier protein, such as KLH during development and to support purification.
The antibody-containing medium is then incubated with the immobilized antigen, either in batch or as the antibody is passed through a column, where it selectively binds and can be retained while impurities are washed away.
[28] These seemingly minute structural changes can affect preclinical stability and process optimization as well as therapeutic product potency, bioavailability and immunogenicity.
The generally accepted purification method of process streams for monoclonal antibodies includes capture of the product target with protein A, elution, acidification to inactivate potential mammalian viruses, followed by ion chromatography, first with anion beads and then with cation beads.
[citation needed] Displacement chromatography has been used to identify and characterize these often unseen variants in quantities that are suitable for subsequent preclinical evaluation regimens such as animal pharmacokinetic studies.
[29][30] Knowledge gained during the preclinical development phase is critical for enhanced product quality understanding and provides a basis for risk management and increased regulatory flexibility.
[34] These techniques can be used to enhance the specificity with which antibodies recognize antigens, their stability in various environmental conditions, their therapeutic efficacy and their detectability in diagnostic applications.
Several successful approaches have been proposed: transgenic mice,[39] phage display[17] and single B cell cloning.
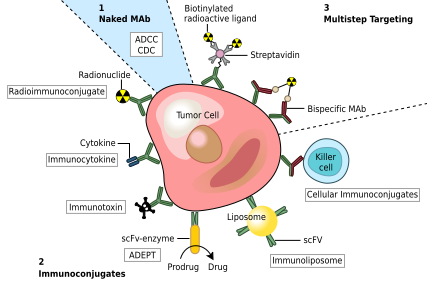
MAbs approved by the FDA for cancer include:[45] Monoclonal antibodies used for autoimmune diseases include infliximab and adalimumab, which are effective in rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and ankylosing spondylitis by their ability to bind to and inhibit TNF-α.
[48][49] In September 2021, the Biden administration purchased US$2.9 billion worth of Regeneron monoclonal antibodies at $2,100 per dose to curb the shortage.
[51] As of December 2021, in vitro neutralization tests indicate monoclonal antibody therapies (with the exception of sotrovimab and tixagevimab/cilgavimab) were not likely to be active against the Omicron variant.
[54] In March 2024, pemivibart, a monoclonal antibody drug, received an emergency use authorization from the US FDA for use as pre-exposure prophylaxis to protect certain moderately to severely immunocompromised individuals against COVID-19.