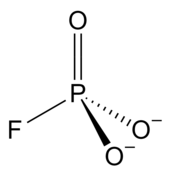
Monofluorophosphate
Organic derivatives can be highly toxic and include diisopropyl fluorophosphate.
Other related nerve gas substances may not be esters, and instead have carbon-phosphorus or nitrogen-phosphorus bonds.
[2] Some of the organic esters are detoxified in mammals by an enzyme in the blood and liver called paraoxonase PON1.
PbO and PbF2 can lower the melting temperature, and increase water resistance.
Phosphoric acid reacts with metal fluorides dissolved in molten urea to yield monofluorophosphates.
[5] Monofluorophosphates are stable at room temperature, but will decompose when heated.
[6] In inorganic compounds the monofluorophosphate ion has an average P–O bond length of 1.51 Å.
[7] Zinc monofluorophosphate can be used as a corrosion inhibitor for steel when salt is present.