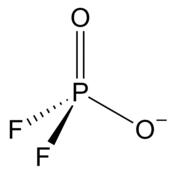
Difluorophosphate
It has a single negative charge and resembles perchlorate (ClO−4) and monofluorosulfonate (SO3F−) in shape and compounds.
[2] Compounds containing difluorophosphate may have it as a simple uninegative ion, it may function as a difluorophosphato ligand where it is covalently bound to one or two metal atoms, or go on to form a networked solid.
[4] It may be covalently bound to a non metal or an organic moiety to make an ester or an amide.
[9] Phosphoryl difluoride oxide also reacts with alkali metal fluorides to yield difluorophosphates.
[14] Irradiating potassium difluorophosphate with gamma rays can make the free radicals •PO2F−, •PO3F− and •PO2F2.
Yet another method involves making difluorphosphoric acid as a side product of calcium fluoride being heated with damp phosphorus pentoxide.
[46] In addition to the isoelectronic series, ions related by substituting fluorine or oxygen by other elements include monofluorophosphate, difluorothiophosphate, dichlorothiophosphate, dichlorophosphate, chlorofluorothiophosphate, chlorofluorophosphate, dibromophosphate, and bromofluorophosphate.
The amines shown to do this include ethylamine, isopropylamine, n-butylamine, t-butylamine, dimethylamine, and diethylamine.