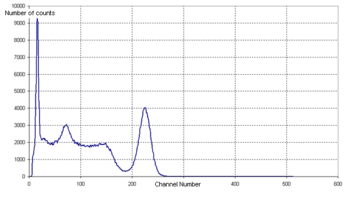
Multichannel analyzer
In alpha-, beta-, and gamma spectroscopy, PHA is used to measure the energy distribution of particles emitted in nuclear decay.
[citation needed] After many pulses have been counted, the output spectrum shows the energy distribution of the radiation incident on the detector.
For example, a Geiger counter connected to an MCA in MCS mode could be used to record the amount of ionizing radiation emitted by a neutron generator at different voltages.
Specialized software processes the "sound" to perform pulse-height analysis and multichannel scaling, forming a complete MCA.
[3] Sound cards have high-speed but low-resolution (up to 192 kHz) ADC chips, allowing for reasonable gamma spectroscopy performance for a low-to-medium count rate.