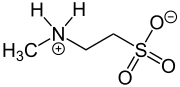
N-Methyltaurine
It is suitable for esterification (actually amide formation) with long-chain carboxylic acids to taurides (acylaminoethansulfonaten) because of its high polarity and the relatively good solubility of its alkaline earth metal salts, which are also used as mild anionic surfactants.
[3] The synthesis of N-methyltaurine was reported as early as 1878,[4] with methylamine being reacted with the silver salt of 2-chloroethanesulfonic acid.
[5] The addition of methylamine to sodium vinylsulfonate in aqueous solution gives N-methyltaurine in 85% yield after acidification with acetic acid.
[6] The purification of the crude product and preparation of the N-methyltaurine can also be accomplished by passage of the sodium salt solution through a cation exchange resin in its H form and then through an anion exchange resin in its OH form.
N-Methyltaurine (or its sodium salt) is used as a polar head group in surfactants from the class of taurides (acylaminoethanesulfonates), sometimes also called methyltaurates.