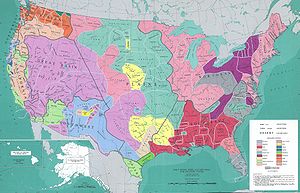
Native American cultures in the United States
Also known as the Columbian interchange, this was the spread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, and ideas between the Americas and the Old World in the 15th and 16th centuries, following Christopher Columbus's 1492 voyage.
The northwest culture area, for example, shared common traits such as salmon fishing, woodworking, large villages or towns, and a hierarchical social structure.
[4] Native Americans in the United States fall into several distinct ethnolinguistic and territorial phyla, with diverse governmental and economic systems.
[6] They may form their own government, enforce laws (both civil and criminal), tax, license and regulate activities, zone, and exclude people from tribal territories.
[7] The traditional diet of Native Americans has historically consisted of a combination of agriculture, hunting, and the gathering of wild foods, variable by bioregion.
Post-contact, European settlers in the northeastern region of the Americas observed that some of the Indigenous peoples cleared large areas for cropland.
Once plants are harvested, traditionally women have prepared the produce for eating, using the maul to grind the corn into mash.
In the American Southwest, especially New Mexico, a syncretism between the Catholicism brought by Spanish missionaries and the Indigenous religions is common; the religious drums, chants, and dances of the Pueblo people are regularly part of Masses at Santa Fe's Saint Francis Cathedral.
[12] Gender roles can vary significantly between tribal nations, with patriarchal, matriarchal, and egalitarian traditions among the 574 federally-recognized tribes.
Others were patrilineal tribes, such as the Omaha, Osage and Ponca, where hereditary leadership passed through the male line, and children were considered to belong to the father and his clan.
Traditionally, Plains women own the home, and tend to jobs such as gathering and cultivating plants for food and healing, along with caring for the young and the elderly, making clothing and processing and curing meat and skins.
[15] In some of the Plains Indian tribes, medicine women gathered herbs and cured the ill.[16] The Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota girls have traditionally been encouraged to learn to ride, hunt and fight.
[17] Though fighting was predominantly the duty of men and boys, occasionally women fought as well, especially if the tribe was severely threatened.
[18] Notable Native American athletes include Jim Thorpe, Joe Hipp, Notah Begay III, Jacoby Ellsbury, and Billy Mills.
The Choctaw called it isitoboli ("Little Brother of War");[19] the Onondaga name was dehuntshigwa'es ("men hit a rounded object").
Some, such as John Trudell, and Blackfoot have used music as political commentary and part of their work as activists for Native American and First Nations causes.
A popular Native American musical form is pow wow drumming and singing, which happens at events like the annual Gathering of Nations in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
[21] Native Americans in the United States have developed several original systems of communication, both in Pre-Columbian times, and later as a response to European influences.
In his system, each symbol represents a syllable rather than a single phoneme; the 85 (originally 86)[26] characters provide a suitable method to write Cherokee.
One case is that of Gonzalo Guerrero, a European from Spain, who was shipwrecked along the Yucatan Peninsula, and fathered three Mestizo children with a Mayan noblewoman.
[30] European impact was immediate, widespread, and profound—more than any other cultural groups that had contact with Native Americans during the early years of colonization and nationhood.
[35] Other North American tribes that participated in some form of enslavement were the Comanche of Texas, the Creek of Georgia, the Pawnee, and Klamath.
As the demand for labor in the West Indies grew with the cultivation of sugar cane, European settlers frequently transported enslaved Native Americans to the Caribbean to work on plantations.
Many surviving Native American peoples of the southeast strengthened their loose coalitions of language groups and joined confederacies such as the Choctaw, the Creek, and the Catawba for protection.
Native American women were at risk for rape whether they were enslaved or not; during the early colonial years, settlers were disproportionately male.
[38] Both Native American and African enslaved women suffered rape and sexual harassment by male slaveholders and other white men.
[40] Among the Five Civilized Tribes, mixed-race slaveholders were generally part of an elite hierarchy, often based on their mothers' clan status, as the societies had matrilineal systems.
As did Benjamin Hawkins, European fur traders and colonial officials tended to marry high-status women, in strategic alliances seen to benefit both sides.
[citation needed] The women's sons gained their status from their mother's families; they were part of hereditary leadership lines who exercised power and accumulated personal wealth in their changing Native American societies.
Native American authors have written about aspects of "tribal philosophy" as opposed to the modern or Western worldview.