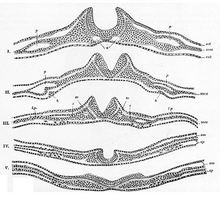
Neural fold
The neural fold is a structure that arises during neurulation in the embryonic development of both birds and mammals among other organisms.
The released calcium interacts with proteins that can modify the actin filaments in the outer epithelial tissue, or ectoderm, in order to induce the dynamic cell movements necessary to create the fold.
[1] When the cells fail to associate in a manner that is not part of the normal course of development, severe diseases can occur.
[7] The molecular mechanism behind this process lies in the expression and repression of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs).
BMPs are a wide family of proteins that perform many functions throughout the growing embryo, including stimulating the growth of cartilage and bone.
[8] The final adhesion of the converging neural folds is due to several different types of intercellular binding proteins.
[1] The neural fold is an extremely important structure in that this mechanism is needed to produce these diverse kinds of cells in the right places.
[12] If the caudal neuropore fails to close, a condition called spina bifida can occur, in which the bottom of the spinal cord remains exposed.