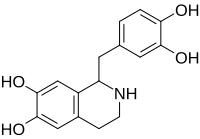
Tetrahydropapaveroline
Tetrahydropapaveroline (norlaudanosoline) is a benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid.
[1] It can be formed in trace amounts in the brain by a condensation reaction of dopamine and dopaldehyde (a metabolite of dopamine).
[1][2] It inhibits dopamine uptake within the cerebral cortex.
[3]