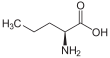
Norvaline
It has previously been reported to be a natural component of an antifungal peptide of Bacillus subtilis.
Norvaline and other modified unbranched chain amino acids have received attention because they appear to be incorporated in some recombinant proteins found in E.
The incorporation of Nva into peptides reflects the imperfect selectivity of the associated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
In Miller–Urey experiments probing prebiotic synthesis of amino acids, norvaline, but also norleucine, are produced.
[4] Norvaline and norleucine (one hydrocarbon group longer) both possess the nor- prefix for historical reason, despite current conventional usage of the prefix to denote a missing hydrocarbon group (under which they would theoretically be called "dihomoalanine" and "trihomoalanine").