Dehydroamino acid
[1] A common dehydroamino acid is dehydroalanine, which otherwise exists only as a residue in proteins and peptides.
The dehydroalanine residue is obtained dehydration of serine-containing protein/peptide (alternatively, removal of H2S from cysteine).
[2] An unusual dehydroamino acid is dehydroglycine (DHG) because it does not contain a carbon-carbon double bond.
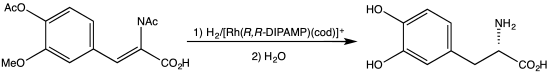
[3] Dehydroamino acids do not feature amino-alkene groups, but the corresponding N-acylated derivatives are known.
The 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to William S. Knowles for his synthesis of L-DOPA from the N-acylacrylate.