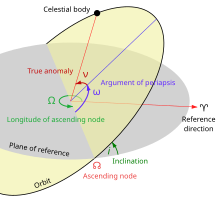
Orbital plane
Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane.
By definition, the reference plane for the Solar System is usually considered to be Earth's orbital plane, which defines the ecliptic, the circular path on the celestial sphere that the Sun appears to follow over the course of a year.
The coordinate system defined that uses the orbital plane as the
Orbital planes of satellites are perturbed by the non-spherical nature of the Earth's gravity.
This causes the orbital plane of the satellite's orbit to slowly rotate around the Earth, depending on the angle the plane makes with the Earth's equator.