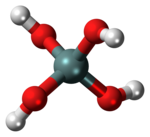
Orthosilicic acid
Typically orthosilicic acid is assumed to be a product of the hydrolysis of its esters, Si(OR)4, where R stands for organyl group, as is practiced in sol-gel syntheses.
[9] Studies have demonstrated that foliar application of stabilized orthosilicic acid can alleviate abiotic stressors such as drought,[10][11] heavy metal toxicity,[12][13] and salinity,[14] resulting in increased yields.
Theoretical computations indicate that the dissolution of silica in water proceeds through the formation of a SiO2·2H2O complex and then orthosilicic acid.
[21][22] These algae polymerise the silicic acid to so-called biogenic silica, used to construct their cell walls (called frustules).
[23] In the uppermost water column the surface ocean is undersaturated with respect to dissolved silica, except for the Antarctic Circumpolar Current south of 55°S.