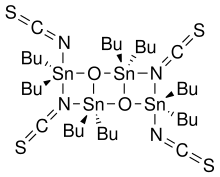
Otera's catalyst
Otera's catalyst, named after Japanese chemist Junzo Otera, is an organostannane compound which has been used as a transesterification catalyst.
[2] This class of compounds may be prepared generally by the reaction of an organotin halide and oxide:[3] In particular, the thiocyanate compound was prepared by the reaction of dibutyltin oxide with dibutyltin diisothiocyanate.
[4][5] In this application, the reaction occurs via the displacement of the bridging isothiocyanate ligands with the incoming alcohol to form an alcohol-bridged active catalyst.
Tin acts as the Lewis acid, and gives the transesterified product.
[2][3] The reaction must be performed in nonpolar solvents in order to colocate the acid and alcohol at the catalytic center.