Ovulation
In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and after the follicular phase.
If no conception occurs, the uterine lining will eventually break down and be shed from the body via the vagina during menstruation.
[3] The signs of ovulation may include cervical mucus changes, mild cramping in the abdominal area, and a small rise in basal body temperature.
[10] In the preovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle, the ovarian follicle will undergo a series of transformations called cumulus expansion, which is stimulated by FSH.
[12][13] For ovulation to be successful, the ovum must be supported by the corona radiata and cumulus oophorous granulosa cells.
Mucification is the secretion of a hyaluronic acid-rich cocktail that disperses and gathers the cumulus cell network in a sticky matrix around the ovum.
[17] Through a signal transduction cascade initiated by LH, which activates the pro-inflammatory genes through cAMP secondary messenger, proteolytic enzymes are secreted by the follicle that degrade the follicular tissue at the site of the blister, forming a hole called the stigma.
The secondary oocyte leaves the ruptured follicle and moves out into the peritoneal cavity through the stigma, where it is caught by the fimbriae at the end of the fallopian tube.
[10] The precise moment of ovulation was captured on film for the first time in 2008, coincidentally, during a routine hysterectomy procedure.
According to the attending gynecologist, the ovum's emergence and subsequent release from the ovarian follicle occurred within a 15-minute timeframe.
The corpus luteum continues this paracrine action for the remainder of the menstrual cycle, maintaining the endometrium, before disintegrating into scar tissue during menses.
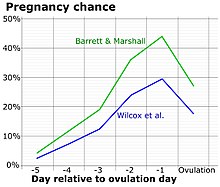
The charting of such symptoms — primarily basal body temperature, mittelschmerz and cervical position — is referred to as the sympto-thermal method of fertility awareness, which allow auto-diagnosis by a female of her state of ovulation.
Once training has been given by a suitable authority, fertility charts can be completed on a cycle-by-cycle basis to show ovulation.
[34] Ovulation induction is a promising assisted reproductive technology for patients with conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and oligomenorrhea.
A low dose of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) may be injected after completed ovarian stimulation.
[36] Combined hormonal contraceptives inhibit follicular development and prevent ovulation as a primary mechanism of action.