Geomagnetic secular variation
Geomagnetic secular variation refers to changes in the Earth's magnetic field on time scales of about a year or more.
[1] The geomagnetic field changes on time scales from milliseconds to millions of years.
[1] In most models, the secular variation is the amortized time derivative of the magnetic field
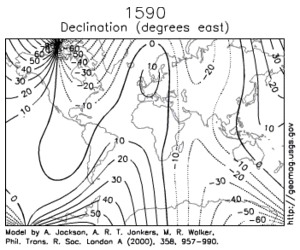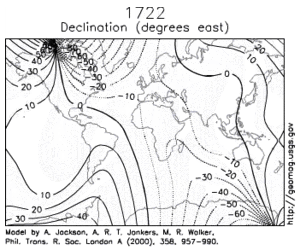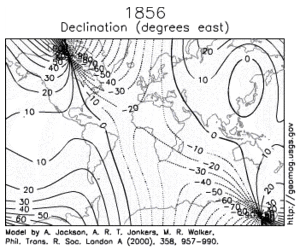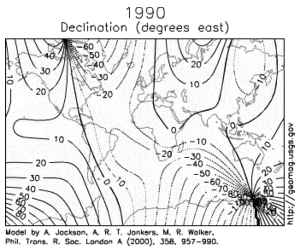
Over such a time scale, magnetic declination is observed to vary over tens of degrees.
[5] A prominent feature in the non-dipolar part of the secular variation is a westward drift at a rate of about 0.2 degrees per year.
[6] Changes that predate magnetic observatories are recorded in archaeological and geological materials.