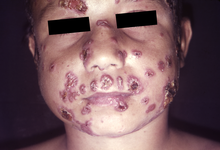
Paracoccidioides lutzii
[4] P. lutzii was formerly classified "PB-01 like", and proposed as a new species in 2014,[5] being discovered in the Central-West region of Brazil.
It forms conidia as part of its life cycle, which cause infection when inhaled into the respiratory tract of humans.
[8] P. lutzii has less adhesion to lung cells than P. brasilensis, potentially explaining its decreased virulence.
[3] It is predominantly distributed in the Central west and Amazon regions of Brazil and Ecuador.
[8] Social and environmental changes, including increased agriculturalization, deforestation in Brazil, expansion of settlements and coffee agriculture could explain the increased incidence of Paracoccidioidies, especially in the Rondônia state of Brazil.